Highway Rail Grade Crossing Risk Assessment Tools

In the U.S., approximately 30% of railroad crashes occur at highway-rail grade crossings (HRGC). Two critical components of the safety risk at HRGCs are the vertical profile of the road segments approaching the grade crossing and the type of commercial motor vehicles (CMVs) traversing a given grade crossing. However, data on the vertical profile of HRGCs and CMV volumes/classifications are limited and infrequently updated. As part of the Federal Railroad Administration’s (FRA) Railroad Information Sharing Environment (RISE), the University of Maryland’s Center for Advanced Transportation Technology (UMD CATT Lab) partnered with the FRA and rail safety stakeholders to address these critical research needs.
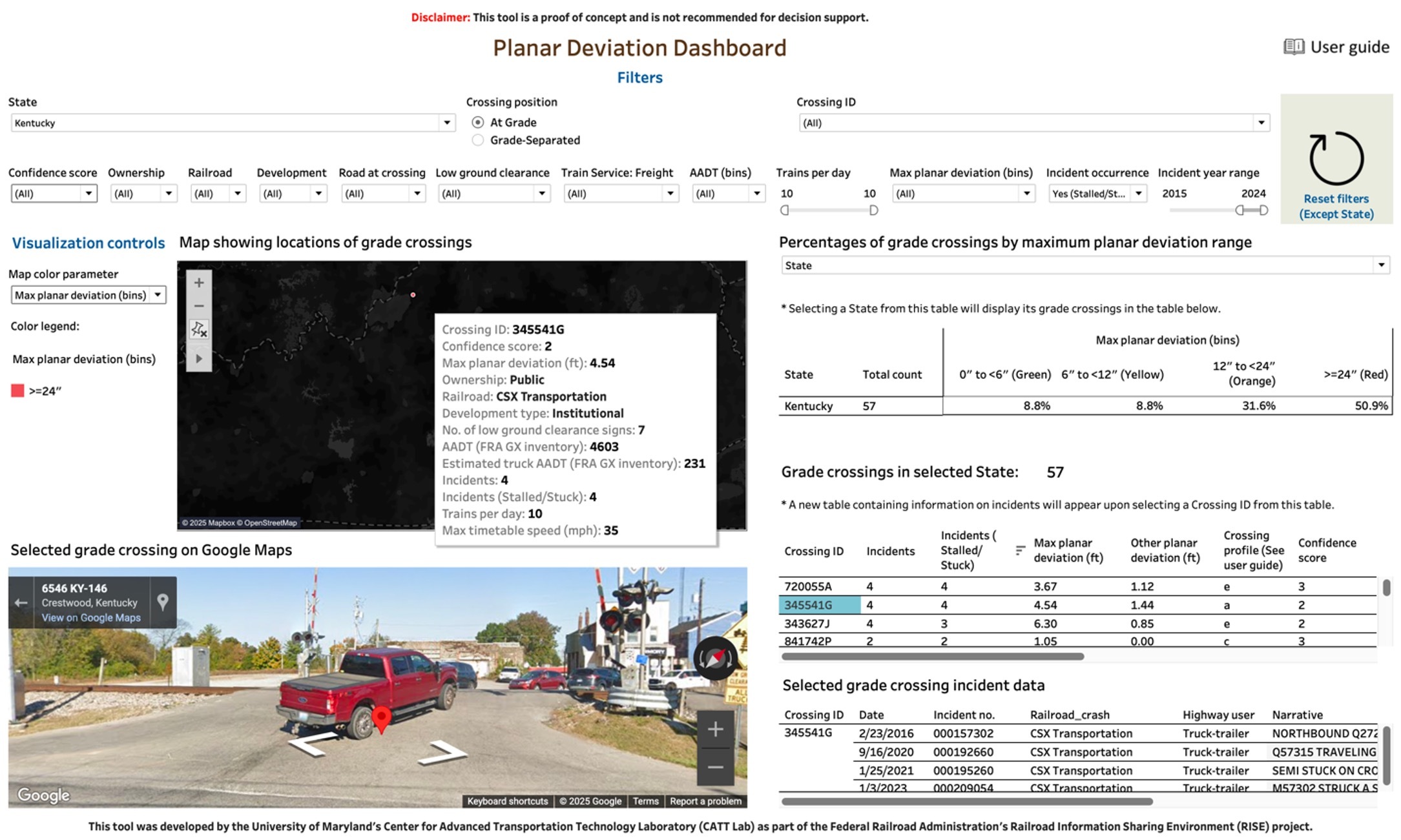
Rail crossing vertical profile estimates
The CATT Lab team developed two products to enable railroad and highway safety stakeholders to identify potentially high-risk HRGCs based on vertical profile estimates and the simulation of design CMVs traversing target HRGCs. First, the team utilized OpenStreetMap (OSM), the North American Rail Network (NARN) and United States Geological Survey (USGS) elevation data to estimate the vertical profiles of every grade crossing in the U.S. These vertical profile estimates were integrated with the FRA Grade Crossing Inventory to build a user-friendly vertical profile dashboard. The dashboard was developed under the guidance of railroad and highway stakeholders to help identify grade crossings to investigate further.
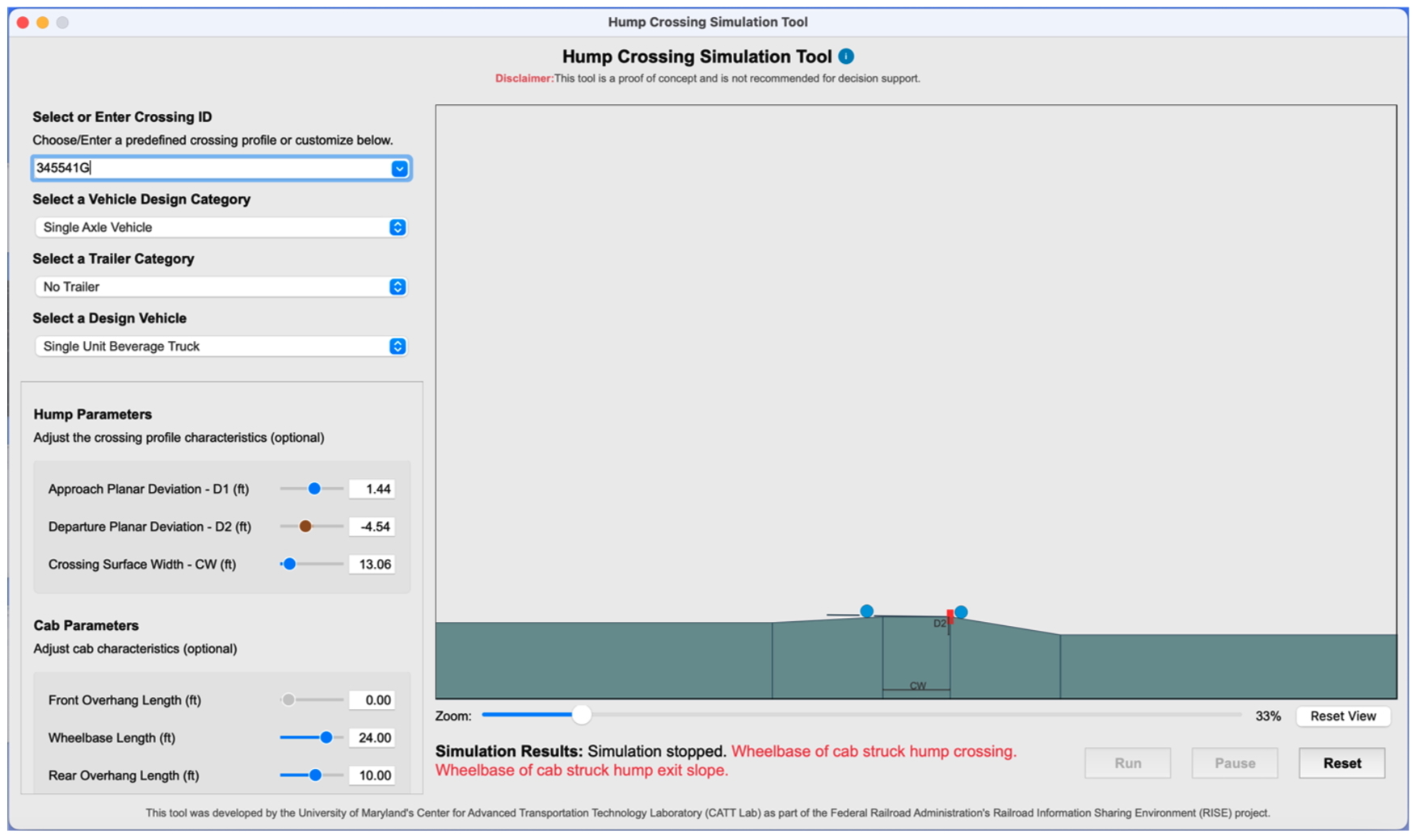
Rail Crossing Simulation Tool
The second product was a tool to simulate CMVs traversing a grade crossing. The simulation tool was developed by leveraging the USGS-based profile estimates with design CMVs from previous studies. Users can select a grade crossing and a design vehicle within the tool to determine if the vehicle makes contact with the crossing surface. The tool also allows users to adjust vertical profiles and vehicle clearance parameters for custom simulations. The simulation tool was designed to be used in coordination with the vertical profile dashboard so users can discover potentially high-risk grade crossings and then simulate various design vehicles traversing the target locations.